Methods of Flow Measurement Apparatus Model FM 106
Home » Products » Methods of Flow Measurement Apparatus Model FM 106
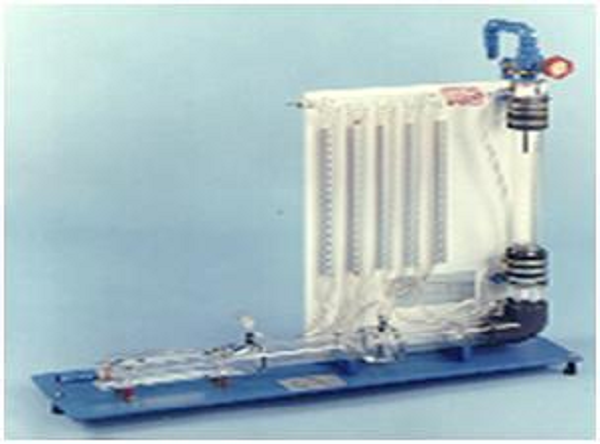
Methods of Flow Measurement Apparatus Model FM 106
With Sci-tech Methods of Flow Measurement Apparatus Model FM 106 students can familiarize themselves with various methods for measuring flow in the pipe system and apply them in practice.
Item Description
Measuring the flow rate is an important aspect in measurement technology. There are several ways to measure the flow of fluids in pipes. The experimental unit contains different measuring instruments to determine the flow rate. These instruments are designed with transparent cases in order to visualize how they operate and function. The methods include, for example, rotameters, a Venturi nozzle or orifice plate flow meter and measuring nozzle. Six tube manometers is used in order to determine the pressure distribution in the Venturi nozzle or the orifice plate flow meter and measuring nozzle. The total pressure is measured by a Pitot tube. The experimental unit is positioned easily and securely on the work surface of the FM 100F Hydraulic Bench. The water is supplied and the flow rate measured by FM 100. Alternatively, the experimental unit can be operated by the laboratory supply.
Features
different methods of flow rate measurement
visualization of the pressure distribution in Venturi nozzle or measuring orifice/measuring nozzle
See also different:

Sci-tech Butterfly Valve & Non-Return Valve Assembly Model FMSC-BVNR are used where flow reversal is not permitted. They must fully seal off the reverse direction while offering the lowest possible resistance in the forward flow direction. [...]

Sci-tech Fluid Mechanics Experimental Plant Model FM 97 allows precise investigations of different fluidic problems. Sci-tech Fluid Mechanics Experimental Plant Model FM 97 allows precise investigations of different fluidic problems. The large [...]

Sci-tech Pressure Distribution Nozzle Performance Study Apparatus Model FM 51 is used to measure pressure curves in convergent and convergent-divergent nozzles (de Laval nozzles) and to study the actual flow of compressible fluids. In addition [...]