Deformation of Curved Axis Beams Model MT 022
Home » Products » Deformation of Curved Axis Beams Model MT 022
Deformation of Curved Axis Beams Model MT 022
In construction engineering, a distinction is made between beams and arches. An arch is a statically indeterminate supported structure with a curved axis and two fixed support bearings or clamp fixings. The support bearings of an arch (such as a double-articulated arch) absorb forces vertically and horizontally. The ends of the arch in the bearings do not move. This produces the static arching effect of the system. In mechanical engineering, crane hooks and chain links are typical examples of a curved beam.
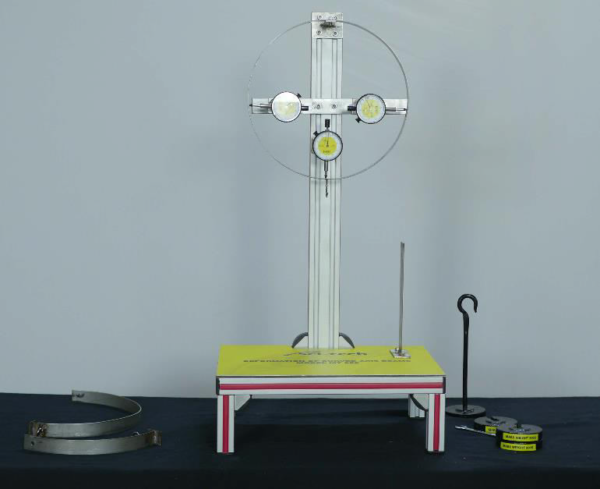
Sci-tech Deformation of Curved-Axis Beams Model MT 022 includes three different beams, borne on statically determinate supports: a circular beam, a semi-circular beam and a quadrant beam.
The beam under test is loaded with a set of weights. Dial gauges record its horizontal and vertical deformations. All three beams have the same cross-section and so the same 2nd moment of area. This enables test results to be directly compared.
Simi-circular and circular beams are fixed to a bearing on the pillar. The quadrant beam is clamped into a bearing block.
The various elements of the experiment are clearly laid-out and housed securely in a storage system.
The well-structured instructional material sets out the fundamentals and provides a step-by-step guide through the experiments.
| Size: | 60cm x 40cm x 80cm (LxWxH) |
| Weight: | 15 kg |
Item Description
Features
* Elastic deformation of curved-axis beams1
* Circular, semi-circular and quadrant beams
In construction engineering, a distinction is made between beams and arches. An arch is a statically indeterminate supported structure with a curved axis and two fixed support bearings or clamp fixings. The support bearings of an arch (such as a double-articulated arch) absorb forces vertically and horizontally. The ends of the arch in the bearings do not move. This produces the static arching effect of the system. In mechanical engineering, crane hooks and chain links are typical examples of a curved beam.
Sci-tech Deformation of Curved-Axis Beams Model MT 022 includes three different beams, borne on statically determinate supports: a circular beam, a semi-circular beam and a quadrant beam.
The beam under test is loaded with a set of weights. Dial gauges record its horizontal and vertical deformations. All three beams have the same cross-section and so the same 2nd moment of area. This enables test results to be directly compared.
Simi-circular and circular beams are fixed to a bearing on the pillar. The quadrant beam is clamped into a bearing block.
The various elements of the experiment are clearly laid-out and housed securely in a storage system.
The well-structured instructional material sets out the fundamentals and provides a step-by-step guide through the experiments.
See also different:

The bending bar in Sci-tech Free Vibration of a Bar Apparatus Model MT 048 can be mounted vertically (standing or hanging) or horizontally into the frame. By varying the free clamping length or moving additional weights, the natural frequency [...]